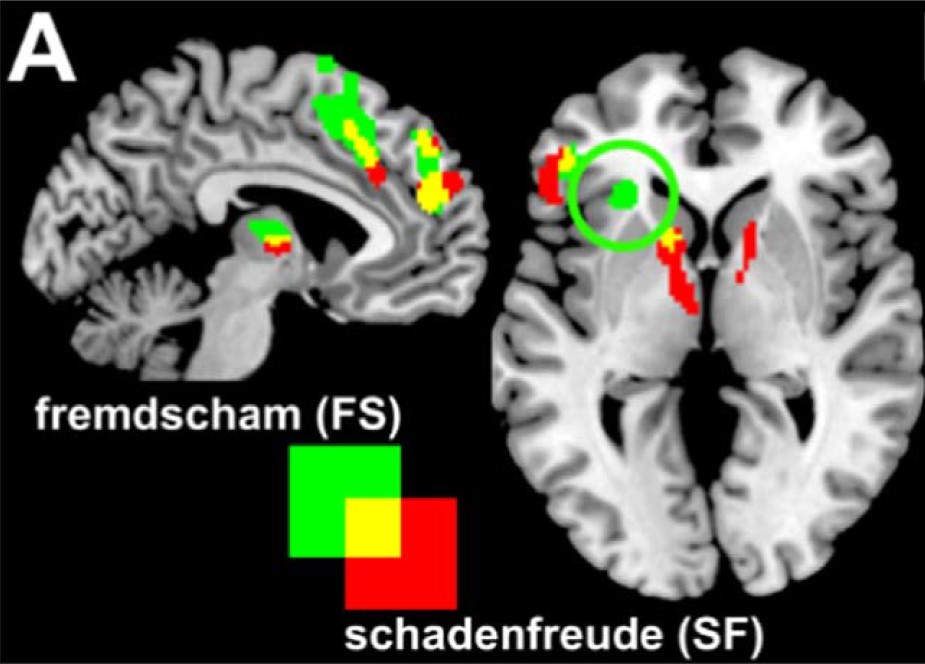
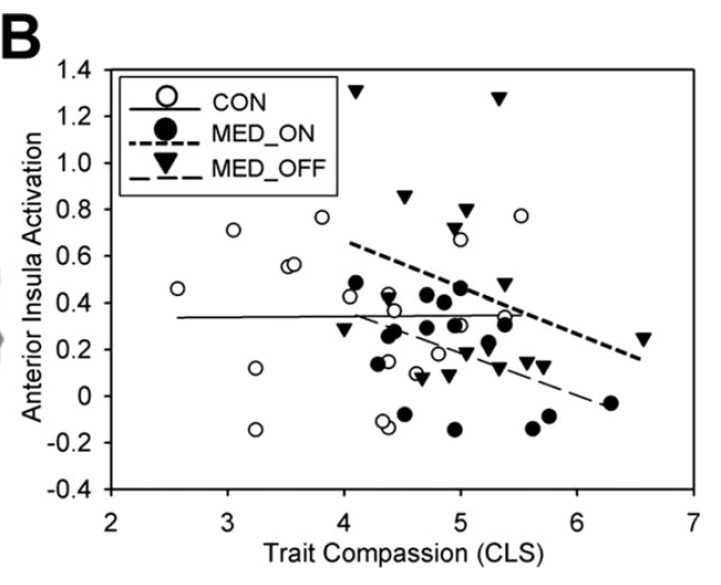
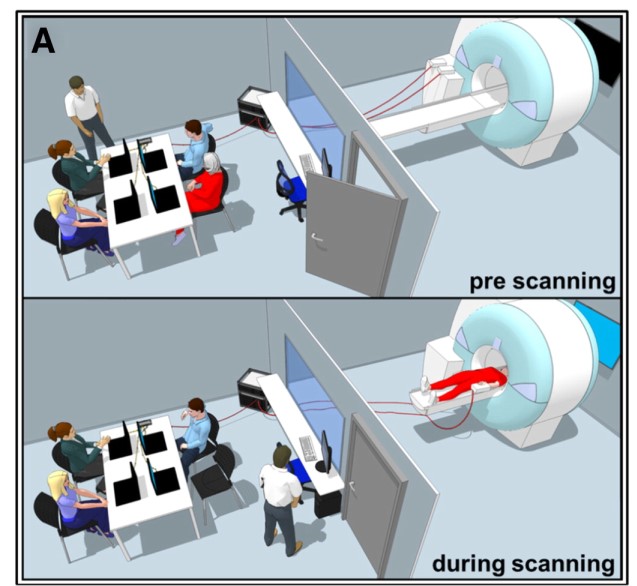
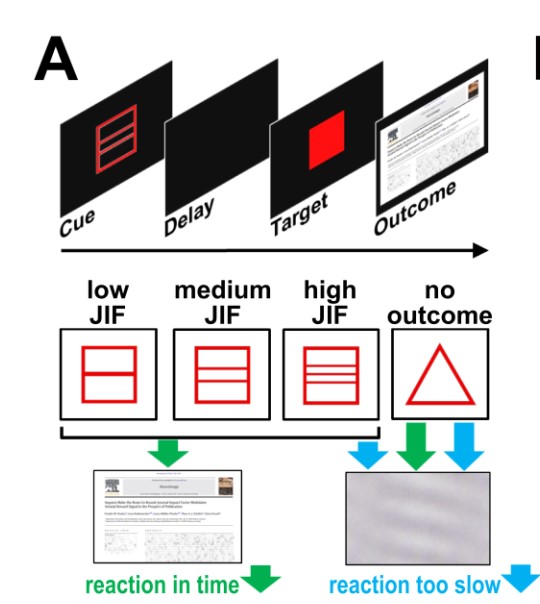
Laugh or cringe? Common and distinct processes of reward-based schadenfreude and empathy-based fremdscham
Abstract Witnessing others’ plights can be funny for observers, but may also trigger one to empathically cringe with the victim of the predicament. In the present study, we examined the common and distinct neural networks involved in schadenfreude (i.e. pleasure derived from another’s misfortune) and fremdscham (i.e. empathically sharing the embarrassment about another’s misfortune). Using […]