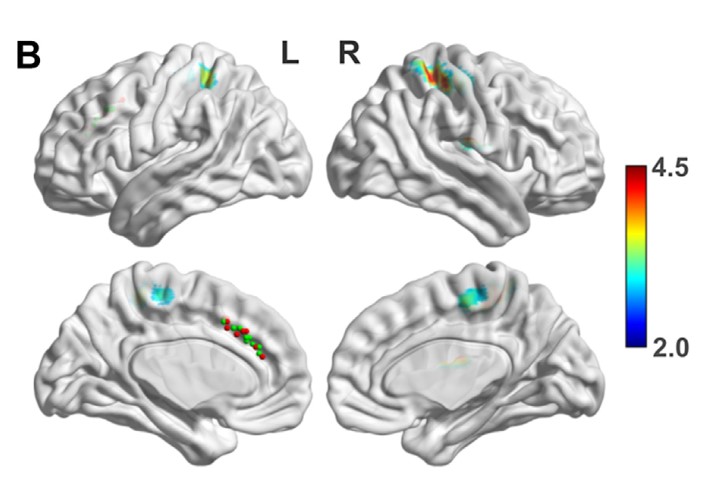
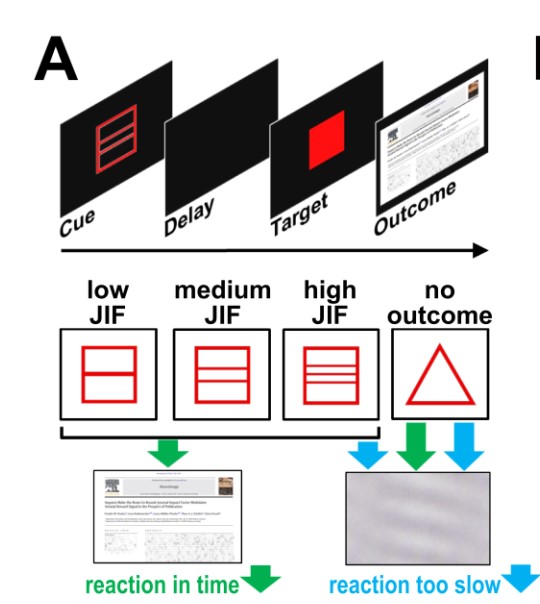
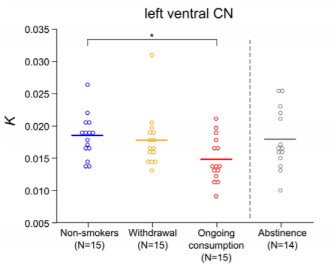
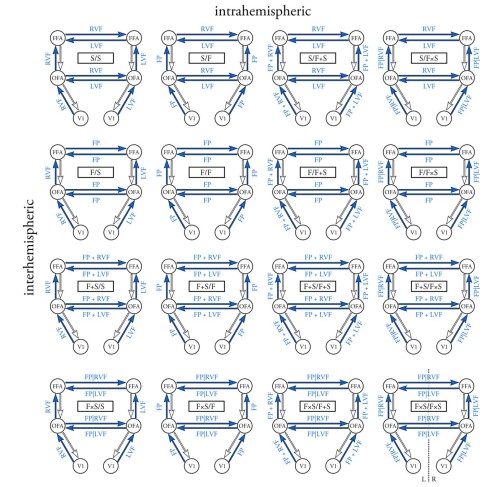
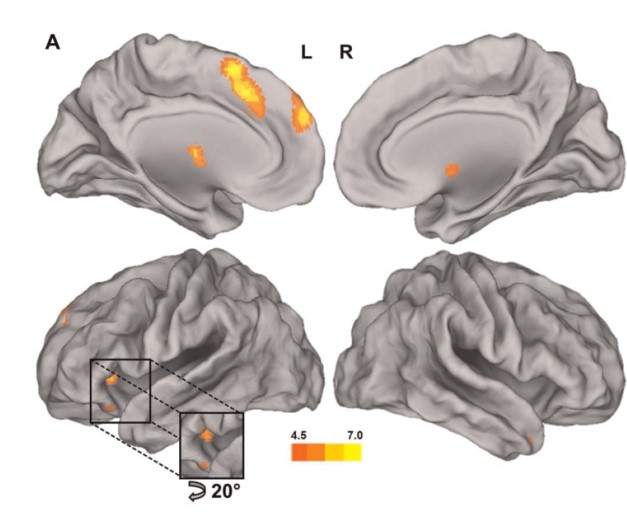
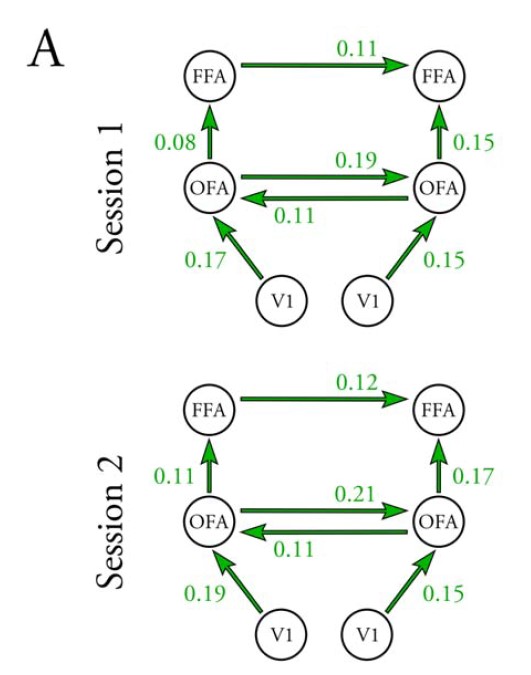
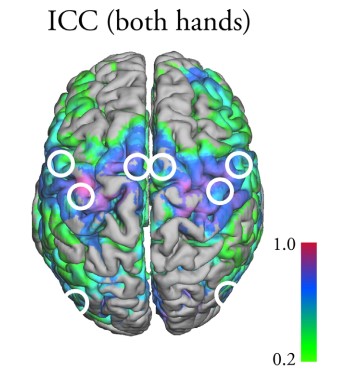
Fronto-insula network activity explains emotional dysfunctions in juvenile myoclonic epilepsy: combined evidence from pupillometry and fMRI
Abstract Emotional instability, difficulties in social adjustment, and disinhibited behavior are the most common symptoms of the psychiatric comorbidities in juvenile myoclonic epilepsy (JME). This psychopathology has been associated with dysfunctions of mesial-frontal brain circuits. The present work is a first direct test of this link and adapted a paradigm for probing frontal circuits during […]