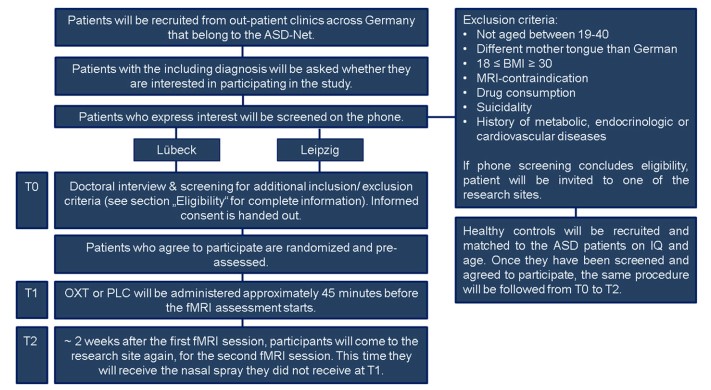
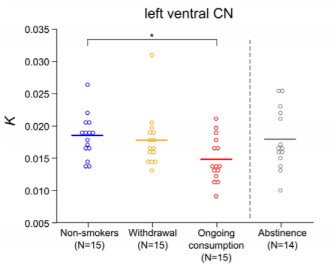
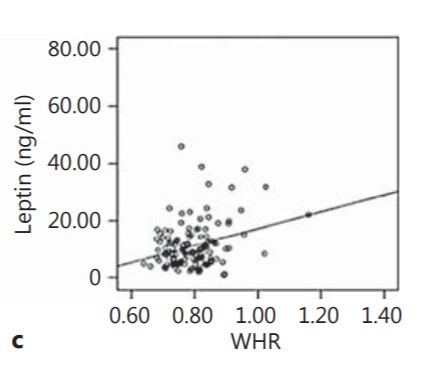
Association of stress-related neural activity and baseline interleukin-6 plasma levels in healthy adults
Abstract Several studies suggest a link between acute changes in inflammatory parameters due to an endotoxin or (psychological) stressor and the brain’s stress response. The extent to which basal circulating levels of inflammatory markers are associated with the brain’s stress response has been hardly investigated so far. In the present study, baseline plasma levels of […]