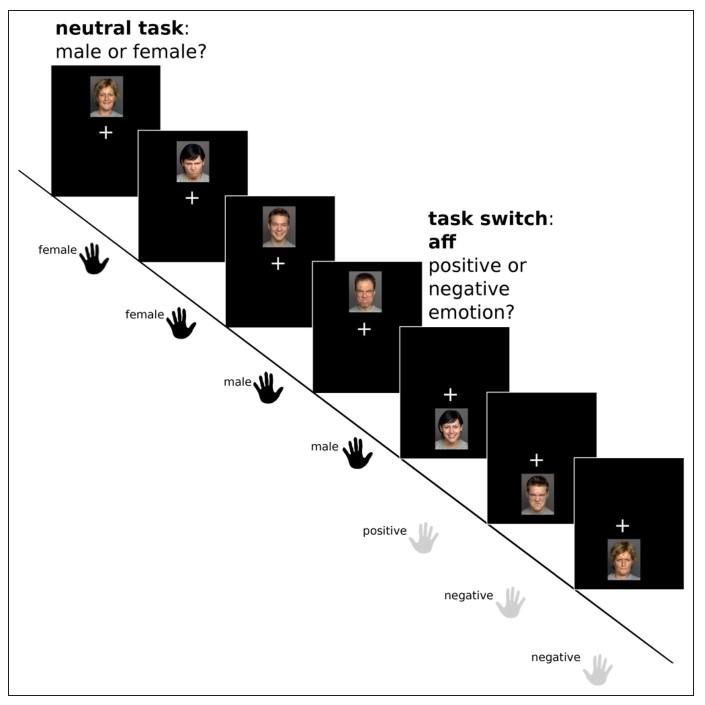
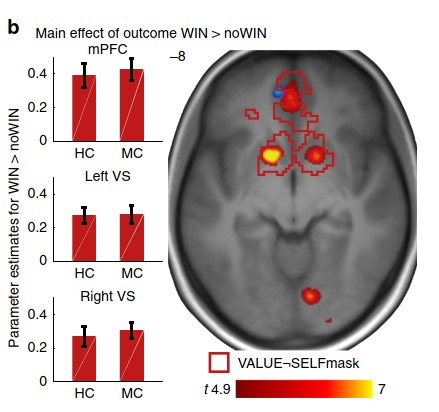
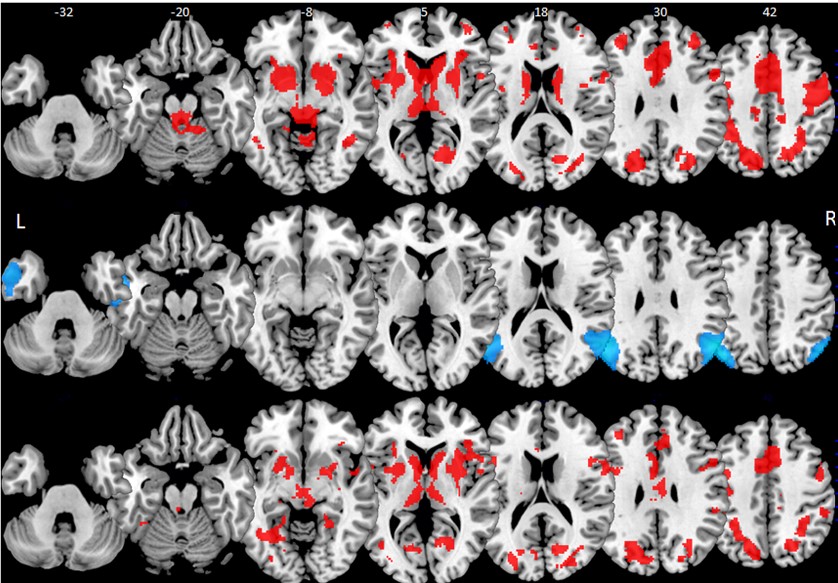
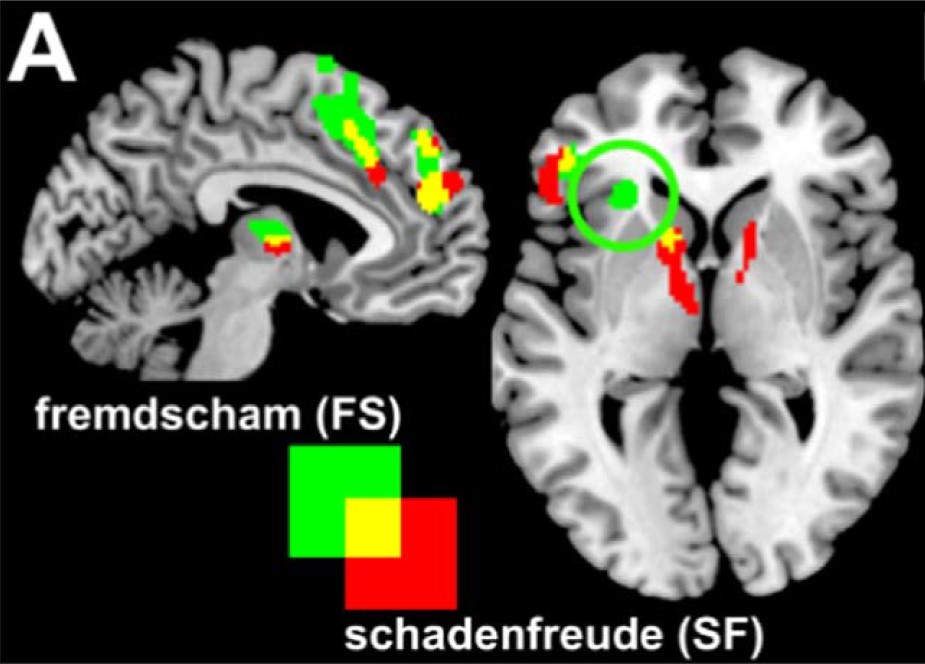
The Human Affectome
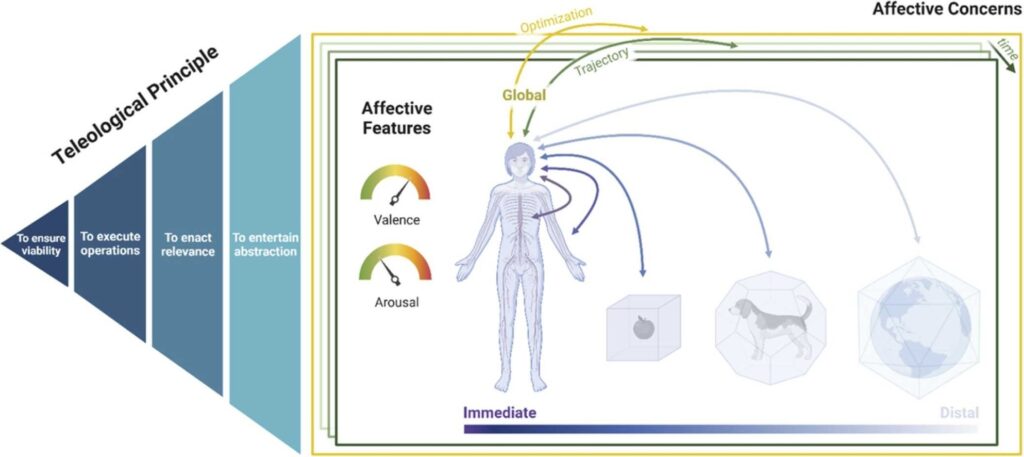
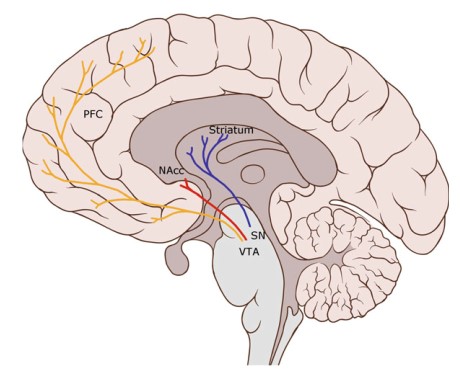
Abstract Over the last decades, the interdisciplinary field of the affective sciences has seen proliferation rather than integration of theoretical perspectives. This is due to differences in metaphysical and mechanistic assumptions about human affective phenomena (what they are and how they work) which, shaped by academic motivations and values, have determined the affective constructs and […]
The Human Affectome Read More »