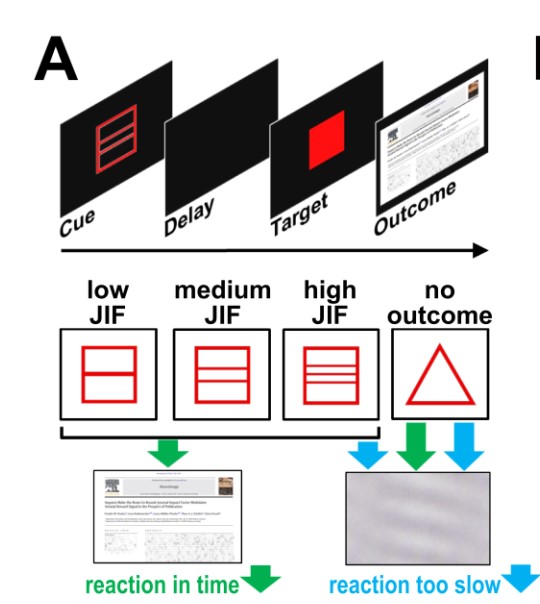
Journal impact factor shapes scientists’ reward signal in the prospect of publication
Abstract The incentive structure of a scientist’s life is increasingly mimicking economic principles. While intensely criticized, the journal impact factor (JIF) has taken a role as the new currency for scientists. Successful goal-directed behavior in academia thus requires knowledge about the JIF. Using functional neuroimaging we examined how the JIF, as a powerful incentive in […]
Journal impact factor shapes scientists’ reward signal in the prospect of publication Read More »