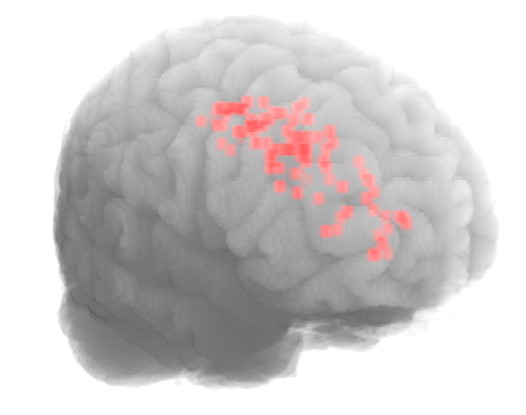
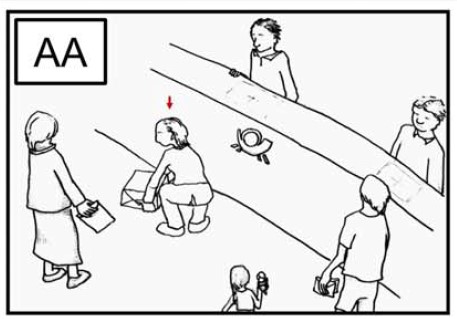
Publications
“The argument from authority tries to justify a conclusion by pointing out that some expert or authority endorses the conclusion. […] “My parents say that Santa Claus exists. Therefore Santa Claus exists” or “My peers say that clothing item x is great. Therefore clothing item x is great.” In the case of the JIF, a high impact factor of a journal would play the role of an authority for the quality of the papers within it.”
- Most recent
- Clinical
- Hormones/Neuromodulators
- Meta-Science (Implications)
- Meta-Science (Methods)
- Social Cognition
- Social Emotions
- Social Learning
- Social Reward
Neural activation during anticipation of opposite-sex and same-sex faces in heterosexual men and women
December 5, 2013
Abstract Psychobiological accounts of face processing predict that greater salience is attributed to faces matching a viewer’s sexual preference than to faces that do not. ...
Read More
Lack of association of a functional catechol-O-methyltransferase gene polymorphism with risk of tobacco smoking: results from a multicenter case-control study
December 5, 2013
Abstract Background: The catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) modulates dopaminergic neurotransmission in the prefrontal cortex as well as in the mesolimbic reward system. Since the reward system mediates addictive ...
Read More
Oxytocin influences processing of socially relevant cues in the ventral tegmental area of the human brain
December 5, 2013
Abstract Background: Evidence accumulates that the neuropeptide oxytocin plays an important role in mediating social interaction among humans and that a dysfunction in oxytocin-modulated brain mechanisms ...
Read More
Concerns about cultural neurosciences: A critical analysis
December 5, 2012
Abstract Ten years ago, neuroscientists began to study cultural phenomena by using functional MRI. Since then the number of publications in this field, termed cultural ...
Read More
Increased autonomic activation in vicarious embarrassment
December 5, 2012
Abstract We studied the somatovisceral response pattern of vicarious embarrassment for someone else’s inappropriate condition. Participants (N=54) were confronted with hand-drawn sketches depicting public situations ...
Read More
Functional connectivity analyses in imaging genetics: considerations on methods and data interpretation
December 5, 2011
Abstract Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) can be combined with genotype assessment to identify brain systems that mediate genetic vulnerability to mental disorders (“imaging genetics”). ...
Read More
Your flaws are my pain: linking empathy to vicarious embarrassment
December 5, 2011
Abstract People vicariously experience embarrassment when observing others’ public pratfalls or etiquette violations. In two consecutive studies we investigated the subjective experience and the neural ...
Read More
Dissociation of neural networks for anticipation and consumption of monetary and social rewards
December 5, 2010
Abstract Human behaviour is generally guided by the anticipation of potential outcomes that are considered to be rewarding. Reward processing can thus be dissected into ...
Read More
Anticipation of monetary and social reward differently activates mesolimbic brain structures in men and women
December 5, 2009
Abstract Motivation for goal-directed behaviour largely depends on the expected value of the anticipated reward. The aim of the present study was to examine how ...
Read More