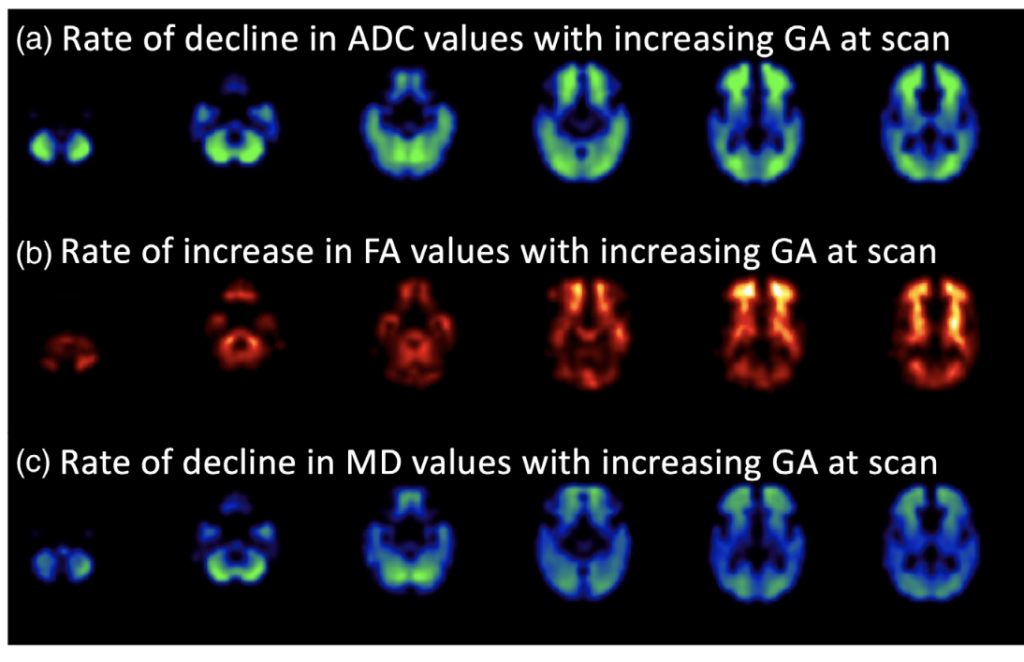
Age-related topographic map of magnetic resonance diffusion metrics in neonatal brains.
Abstract Accelerated maturation of brain parenchyma close to term-equivalent age leads to rapid changes in diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) metrics of neonatal brains, which can complicate the evaluation and interpretation of these scans. In this study, we characterized the topography of age-related evolution of diffusion metrics in neonatal brains. We included […]
Age-related topographic map of magnetic resonance diffusion metrics in neonatal brains. Read More »