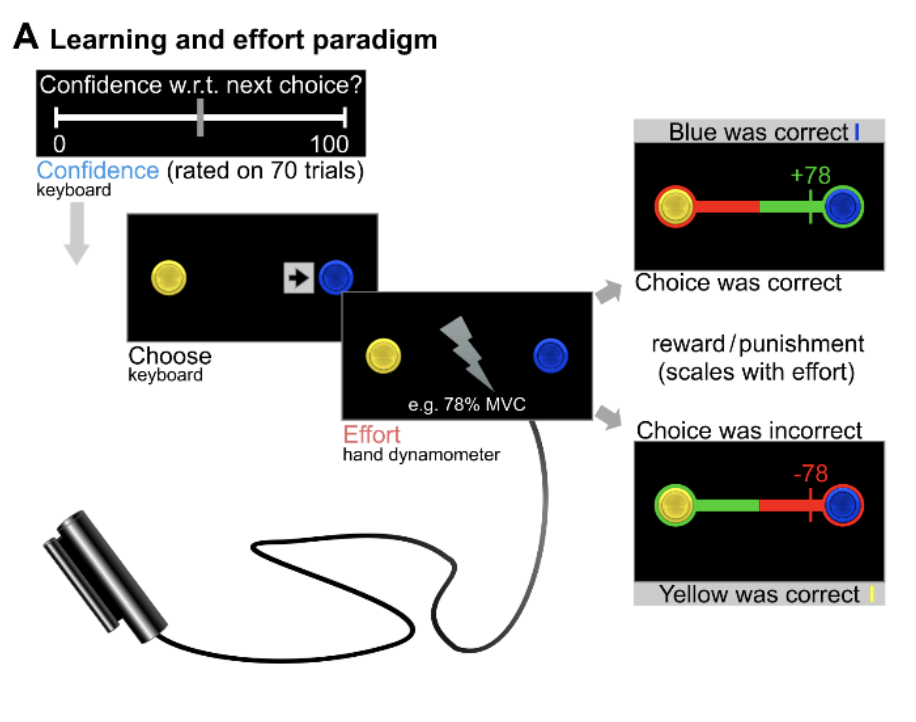
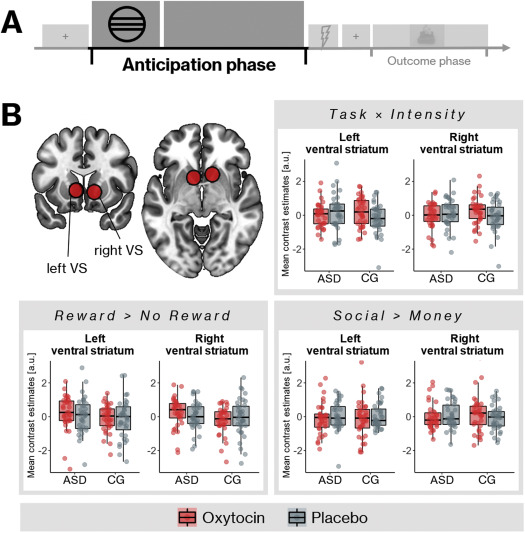
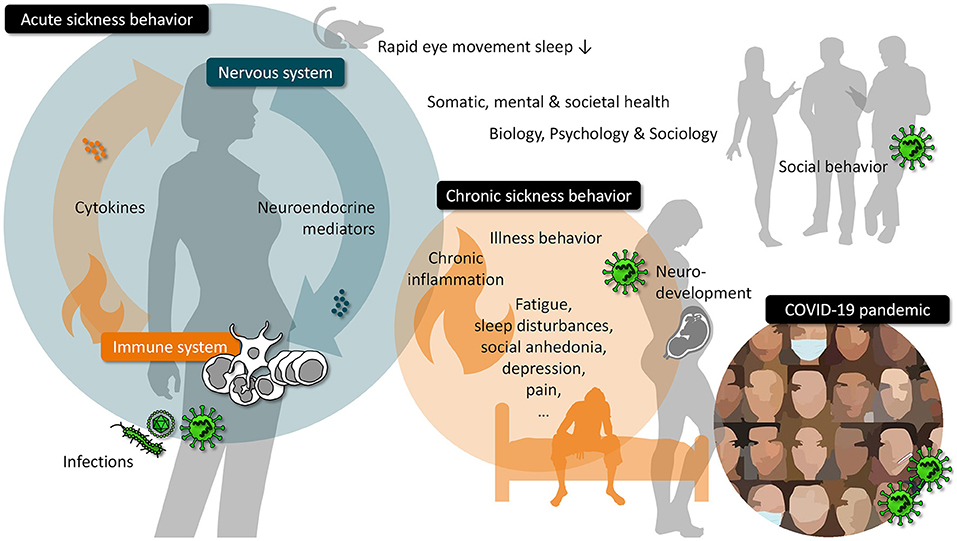
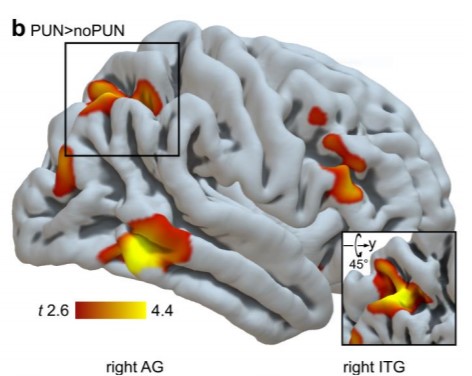
The (un)learning of social functions and its significance for mental health
Abstract Social interactions are dynamic, context-dependent, and reciprocal events that influence prospective strategies and require constant practice and adaptation. This complexity of social interactions creates several research challenges. We propose a new framework encouraging future research to investigate not only individual differences in capacities relevant for social functioning and their underlying mechanisms, but also the […]
The (un)learning of social functions and its significance for mental health Read More »