Publications
“The argument from authority tries to justify a conclusion by pointing out that some expert or authority endorses the conclusion. […] “My parents say that Santa Claus exists. Therefore Santa Claus exists” or “My peers say that clothing item x is great. Therefore clothing item x is great.” In the case of the JIF, a high impact factor of a journal would play the role of an authority for the quality of the papers within it.”
- Most recent
- Clinical
- Hormones/Neuromodulators
- Meta-Science (Implications)
- Meta-Science (Methods)
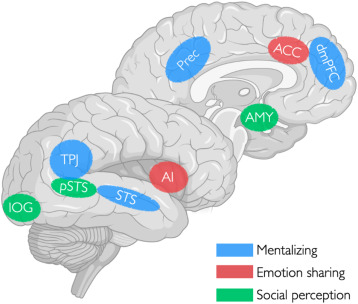
- Social Cognition
- Social Emotions
- Social Learning
- Social Reward
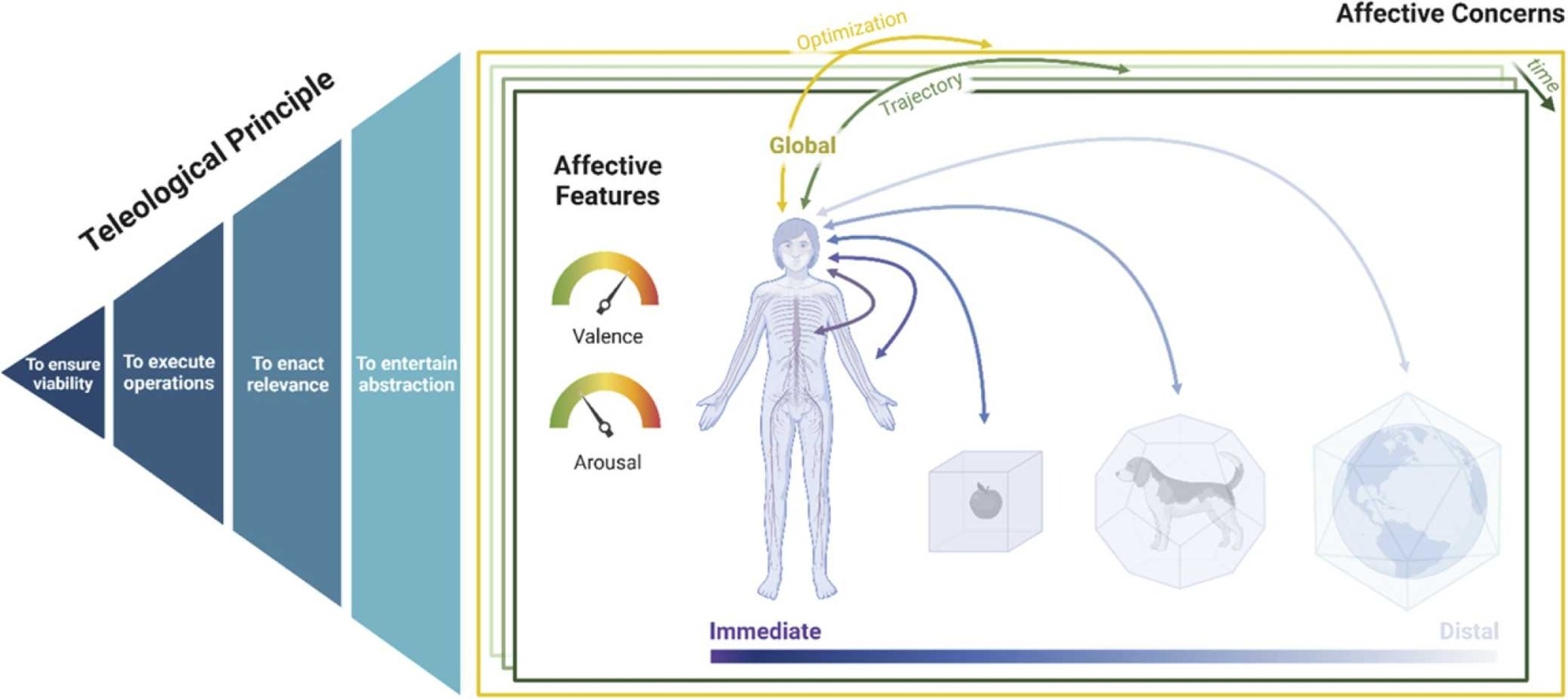
The Human Affectome
November 3, 2023
Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews
Abstract Over the last decades, the interdisciplinary field of the affective sciences has seen proliferation rather than integration of theoretical perspectives. This is due to ...
Read More
Rethink funding by putting the lottery first
June 22, 2023
Nature Human Behaviour
Rethink funding Researchers propose a new way to restructure grant allocation, promoting inclusivity, innovation, and cost reduction. LÜBECK UNIVERSITY, Germany – The allocation process of ...
Read More
On the potentials of interaction breakdowns for HRI
April 5, 2023
Behavioral Brain Sciences
Abstract How do we switch between “playing along” and treating robots as technical agents? We propose interaction breakdowns to help solve this “social artifact puzzle”: ...
Read More
Individual differences in resilience to stress are associated with affective flexibility
December 19, 2022
Psychological Research
Abstract Cognitive flexibility is frequently linked to resilience because of its important contribution to stress regulation. In this context, particularly affective flexibility, defined as the ...
Read More
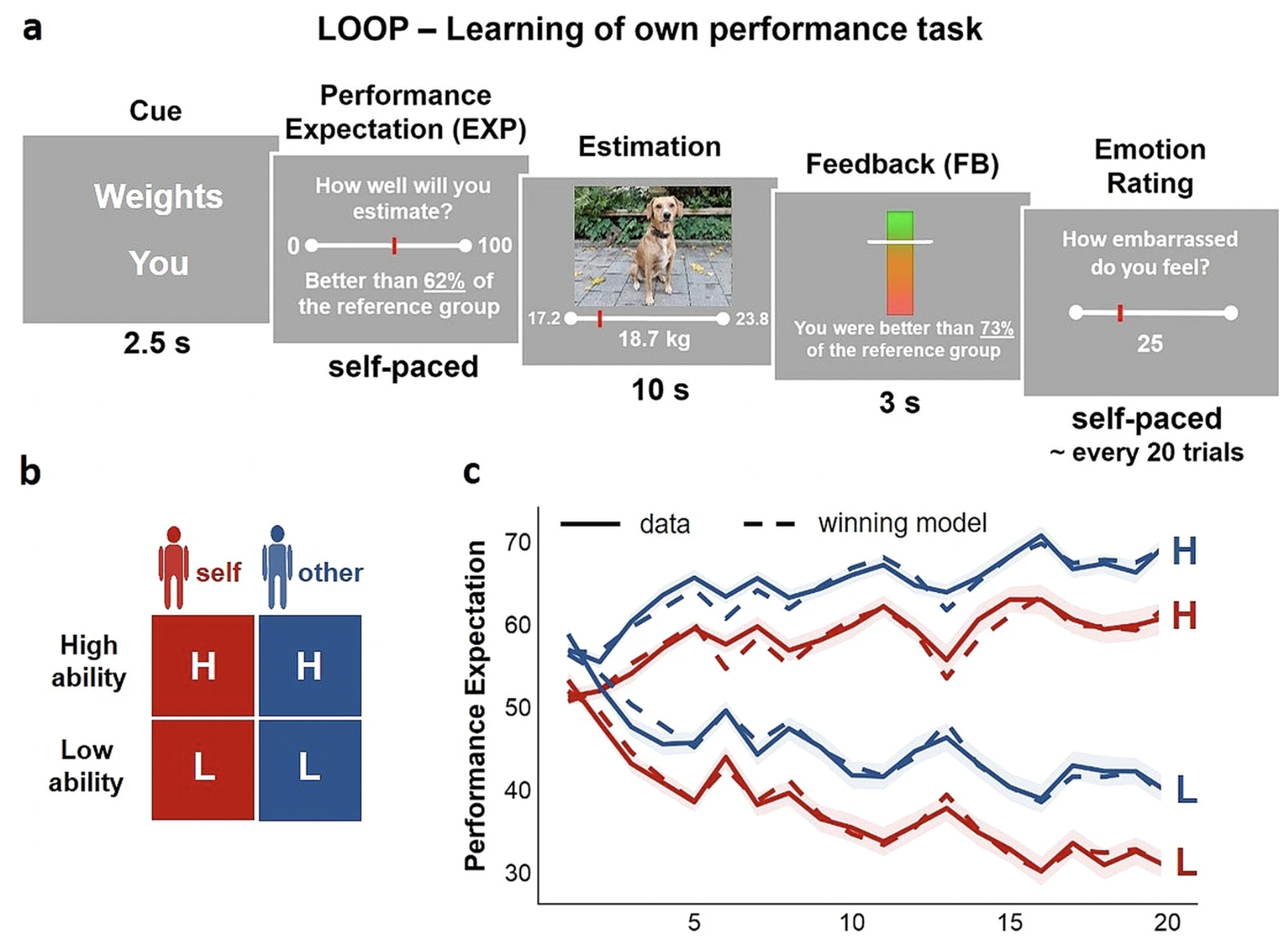
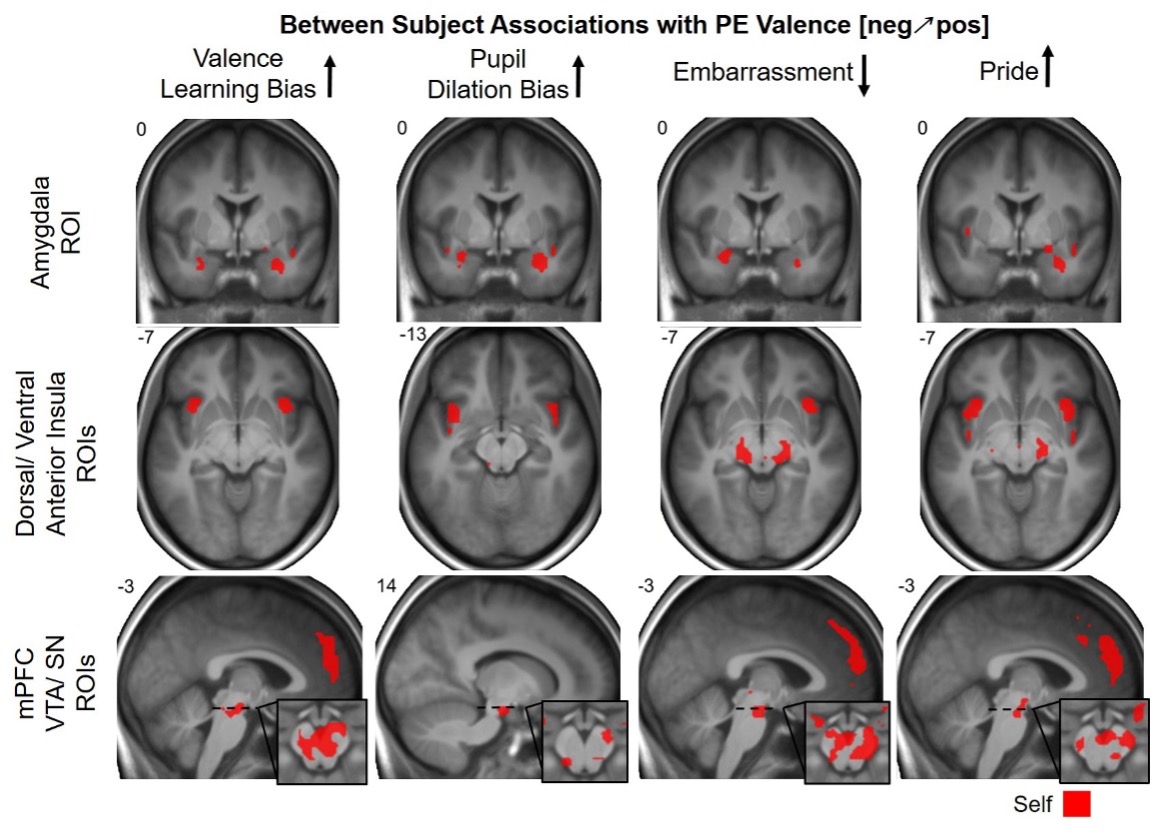
Neurocomputational mechanisms of affected beliefs
November 14, 2022
Communications Biology
Abstract The feedback people receive on their behavior shapes the process of belief formation and self-efficacy in mastering a particular task. However, the neural and ...
Read More
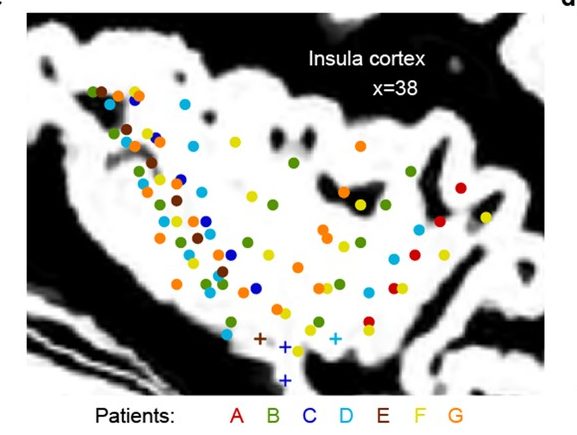
Intracranial human recordings reveal association between neural activity and perceived intensity for the pain of others in the insula
November 4, 2022
eLife
Abstract Based on neuroimaging data, the insula is considered important for people to empathize with the pain of others. Here we present intracranial electroencephalographic (iEEG) ...
Read More
The (un)learning of social functions and its significance for mental health
October 19, 2022
Clinical Psychology Review
Abstract Social interactions are dynamic, context-dependent, and reciprocal events that influence prospective strategies and require constant practice and adaptation. This complexity of social interactions creates ...
Read More
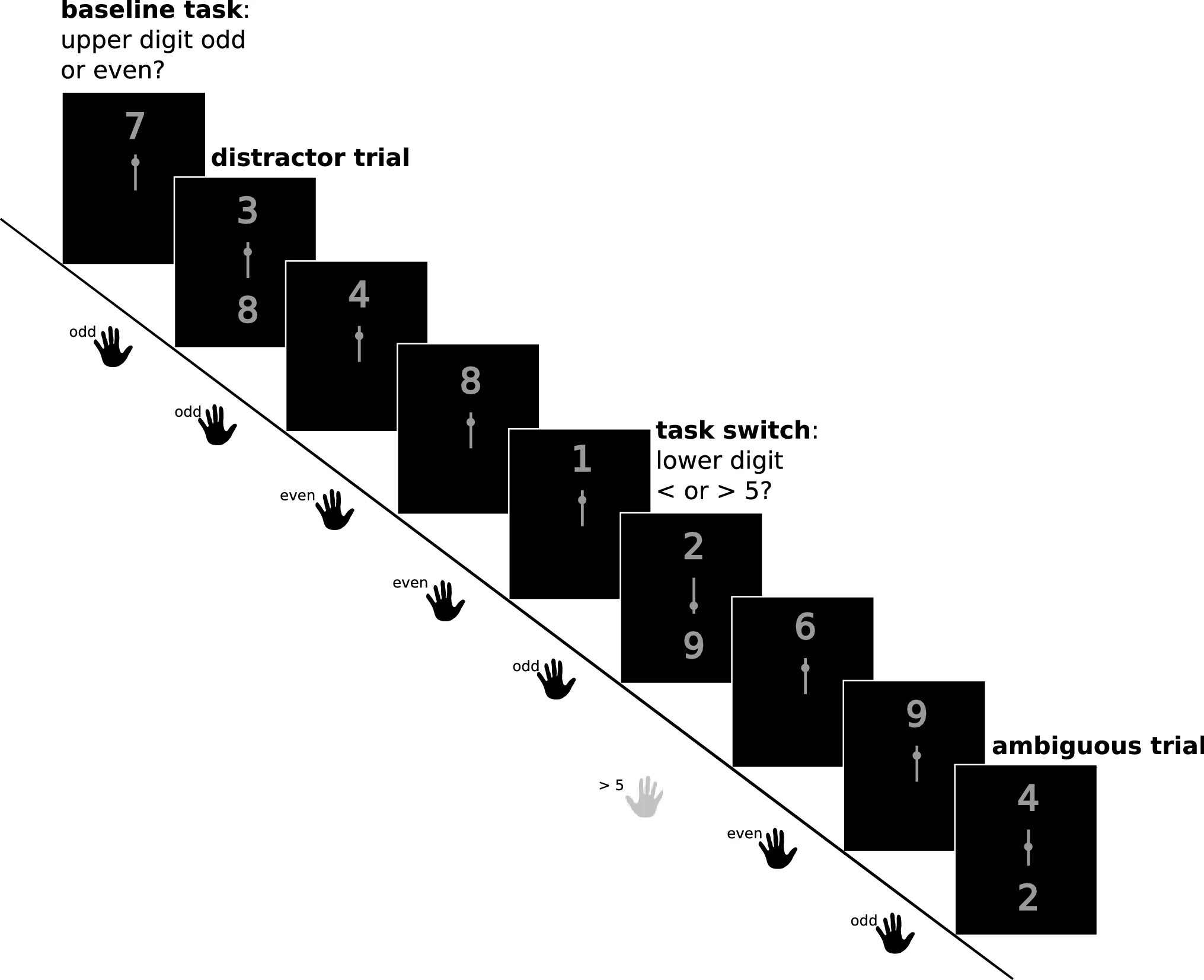
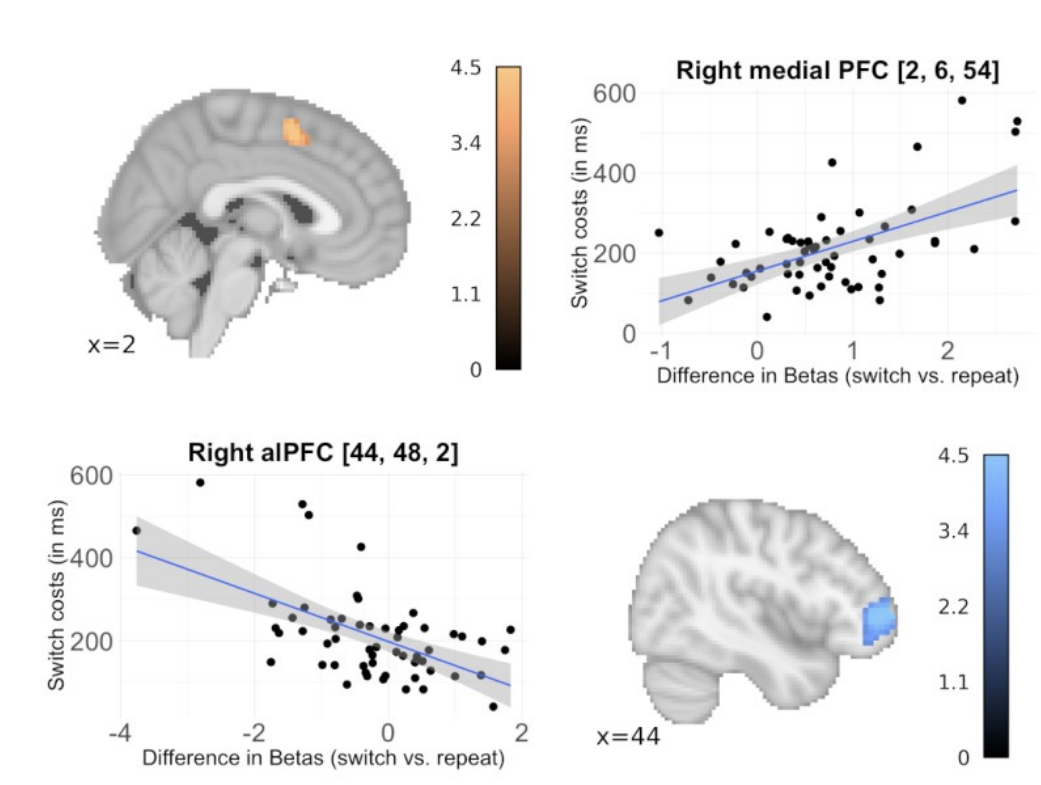
Neural correlates of affective task switching and asymmetric affective task switching costs
October 13, 2022
Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience
Abstract The control of emotions is of potentially great clinical relevance. Accordingly, there has been increasing interest in understanding the cognitive mechanisms underlying the ability ...
Read More
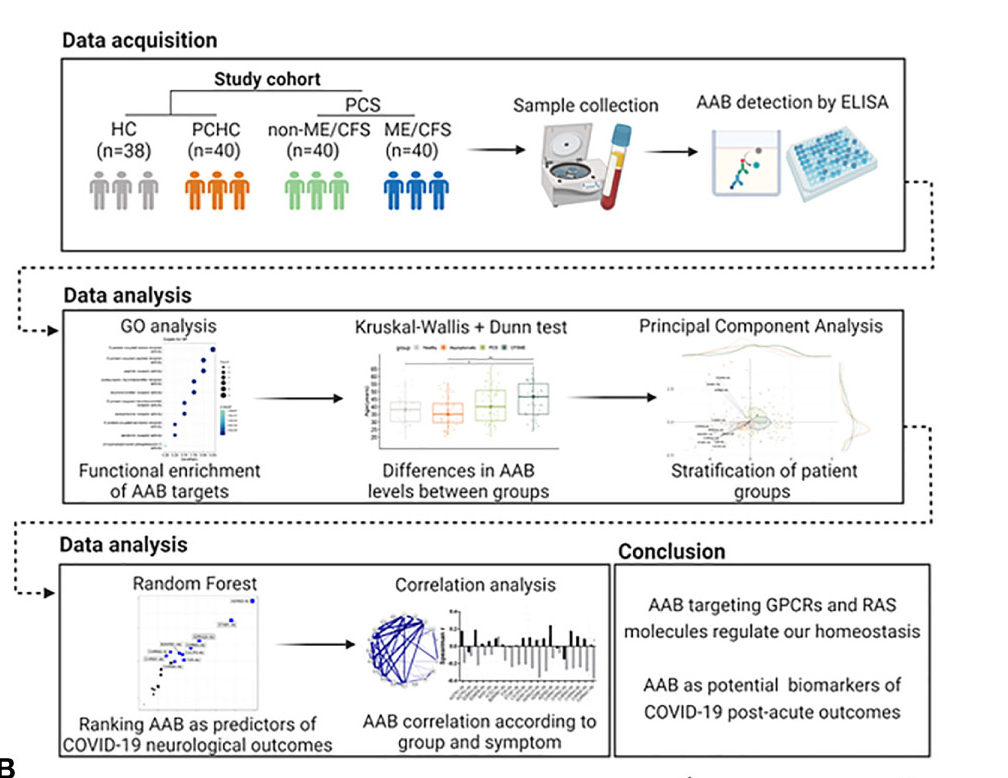
Dysregulated autoantibodies targeting vaso- and immunoregulatory receptors in Post COVID Syndrome correlate with symptom severity
September 27, 2022
Frontiers in Immunology
Abstract Most patients with Post COVID Syndrome (PCS) present with a plethora of symptoms without clear evidence of organ dysfunction. A subset of them fulfills ...
Read More
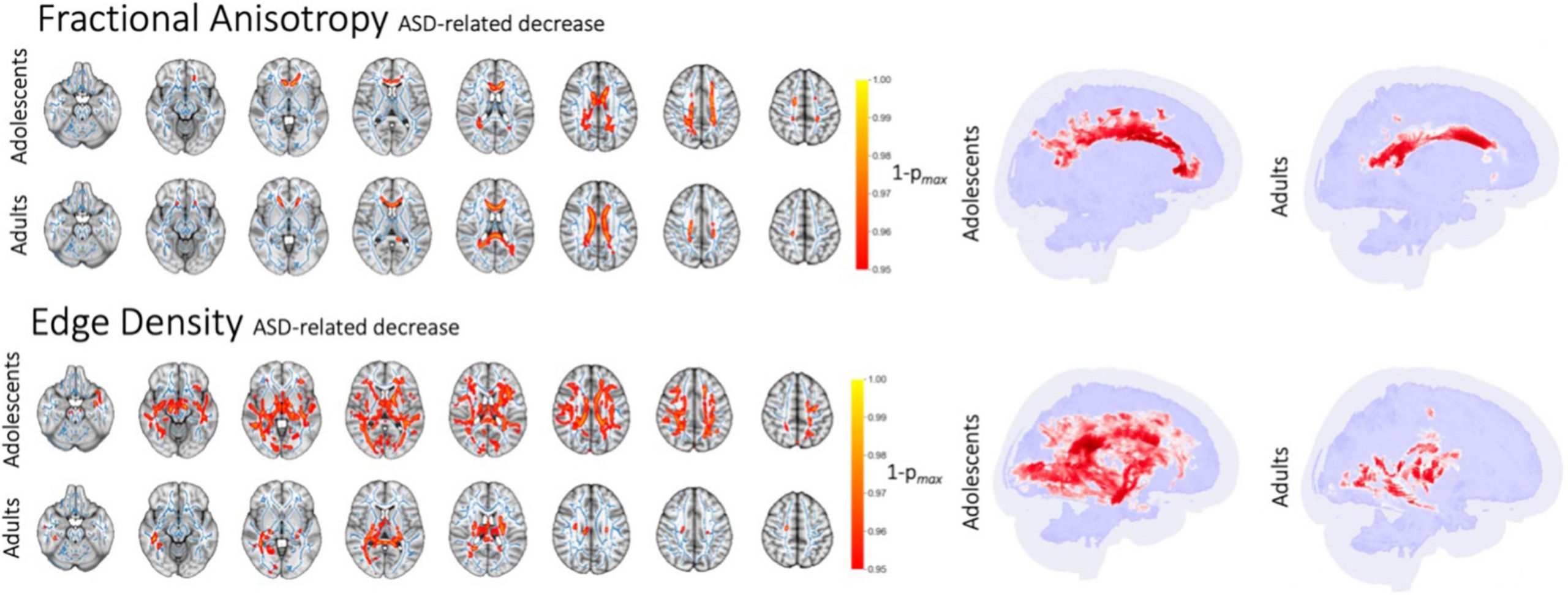
Age-dependent white matter microstructural disintegrity in autism spectrum disorder
September 7, 2022
Frontiers in Neurology
Abstract There has been increasing evidence of White Matter (WM) microstructural disintegrity and connectome disruption in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). We evaluated the effects of ...
Read More
Mapping Research Domain Criteria using a transdiagnostic mini-RDoC assessment in mental disorders
July 20, 2022
Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci
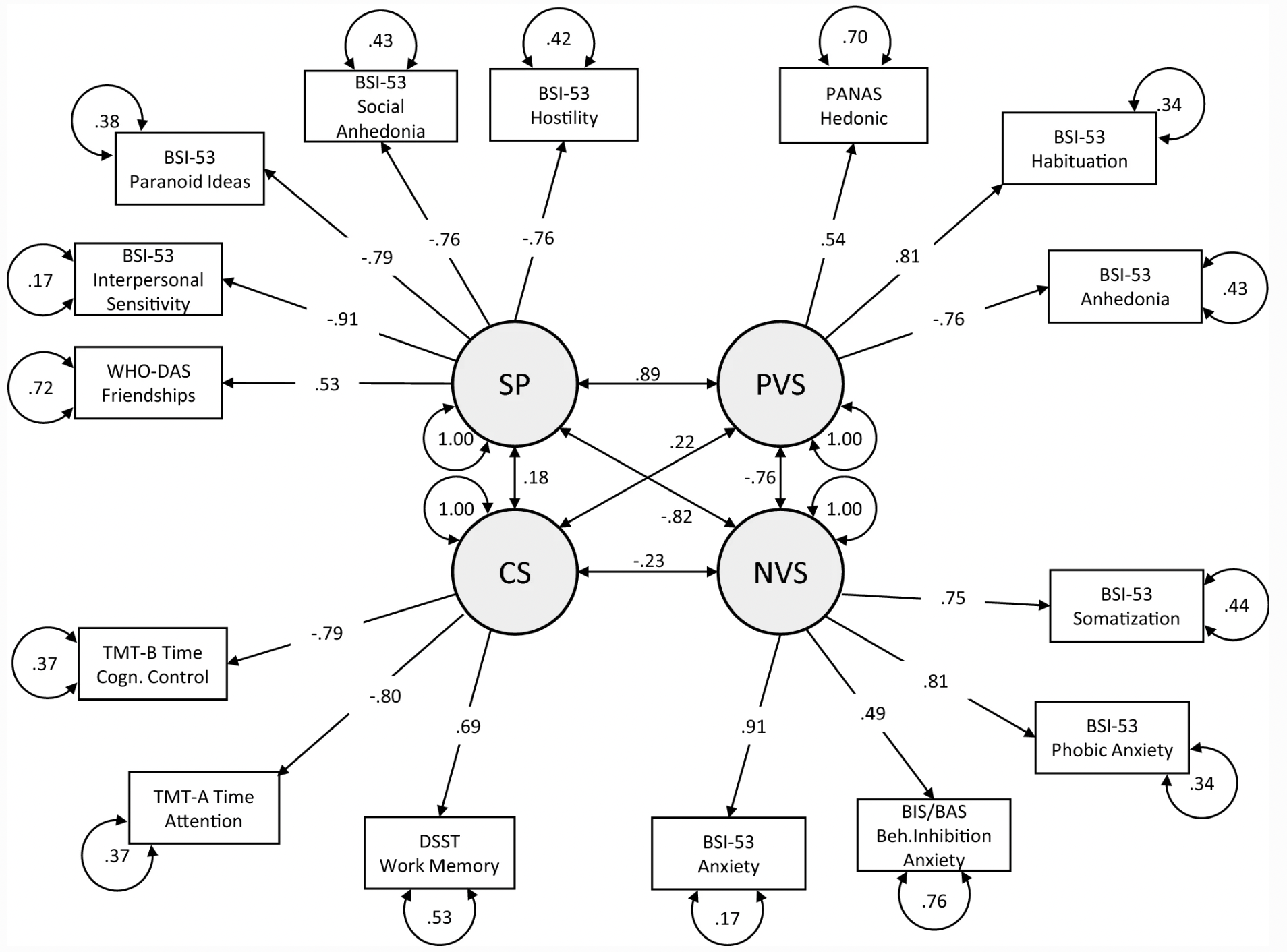
Abstract This study aimed to build on the relationship of well-established self-report and behavioral assessments to the latent constructs positive (PVS) and negative valence systems ...
Read More
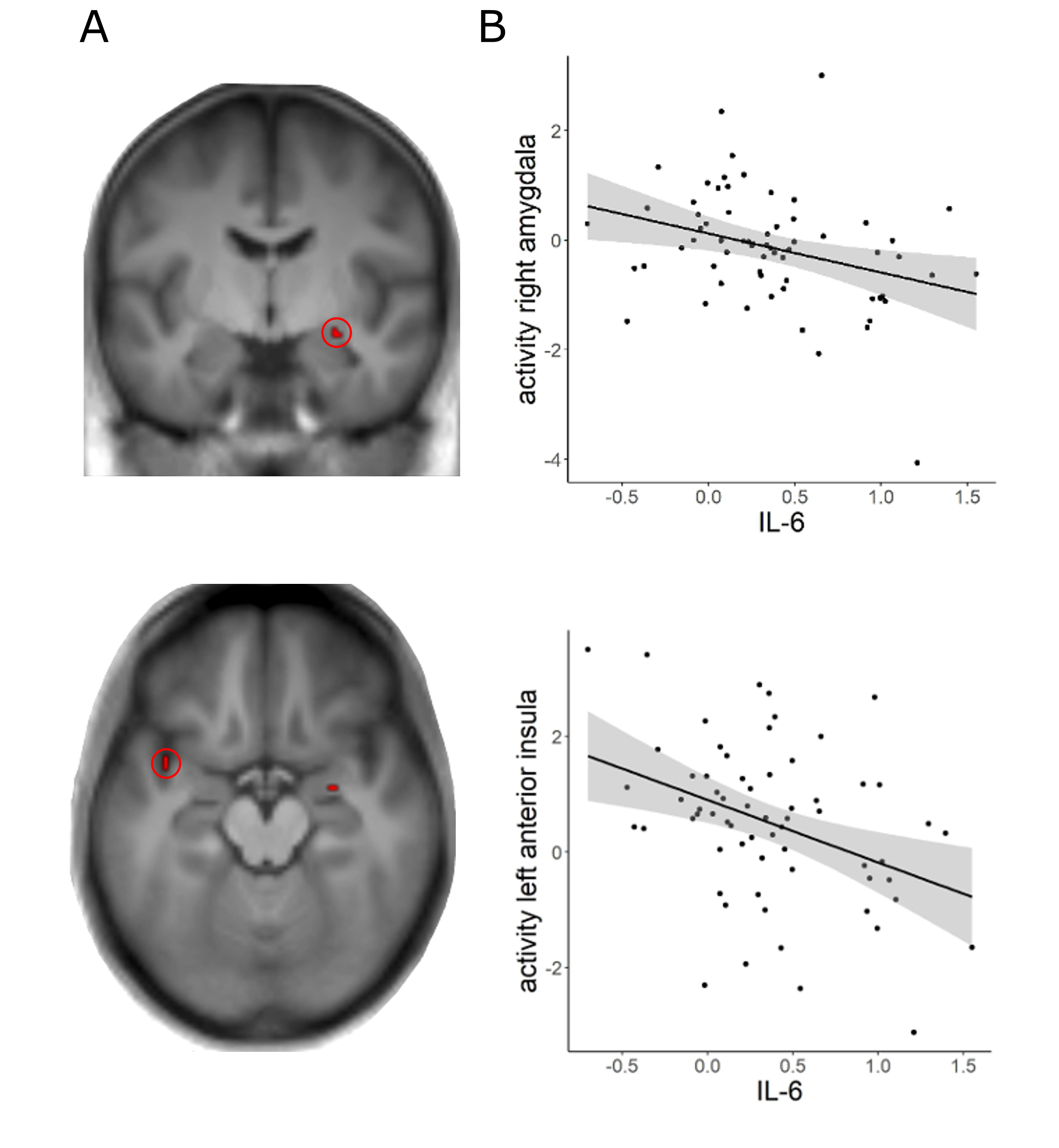
Association of stress-related neural activity and baseline interleukin-6 plasma levels in healthy adults
Abstract Several studies suggest a link between acute changes in inflammatory parameters due to an endotoxin or (psychological) stressor and the brain’s stress response. The ...
Read More
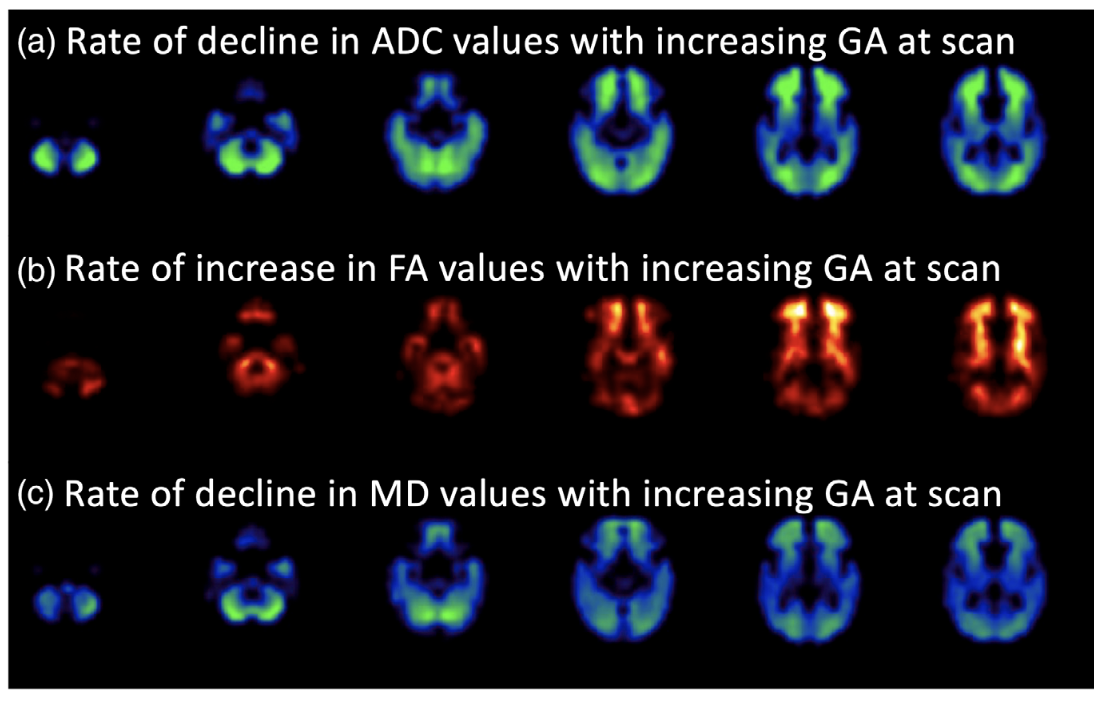
Age-related topographic map of magnetic resonance diffusion metrics in neonatal brains.
May 23, 2022
Human Brain Mapping
Abstract Accelerated maturation of brain parenchyma close to term-equivalent age leads to rapid changes in diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) metrics of ...
Read More
Determinants of motivated behavior are linked to fatigue and its perturbation by SARS-CoV-2 vaccination
April 27, 2022
medRxiv
Abstract Background Fatigue has an adaptive function and serves as a temporary signal to rest and save energy often in response to immune activation. It may, ...
Read More
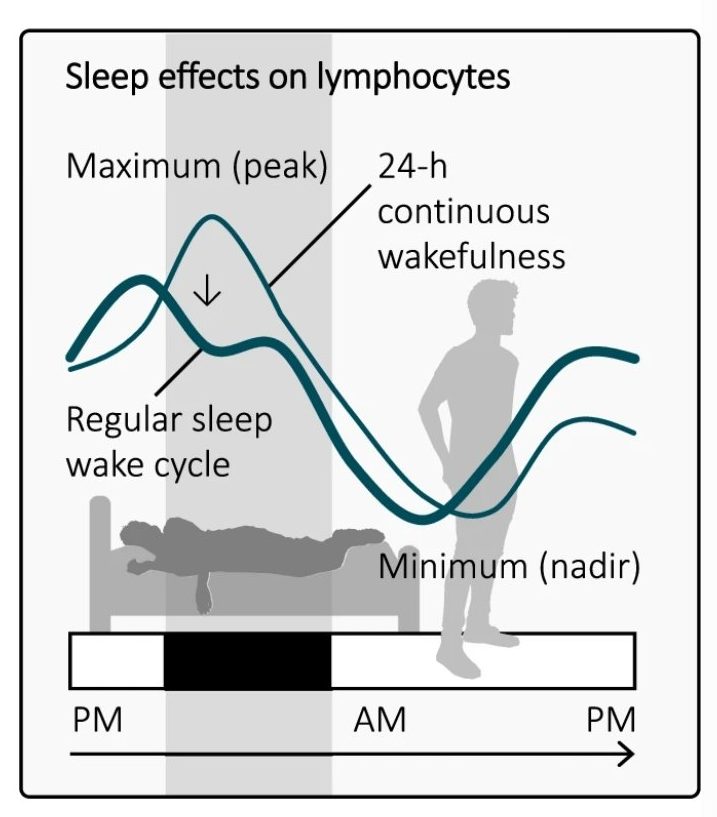
The contribution of sleep to the neuroendocrine regulation of rhythms in human leukocyte traffic
January 28, 2022
Seminars in Immunopathology
Abstract Twenty-four-hour rhythms in immune parameters and functions are robustly observed phenomena in biomedicine. Here, we summarize the important role of sleep and associated parameters ...
Read More
Neurocomputational mechanisms of affected beliefs
November 1, 2021
bioRxiv
We are truely excited about our new preprint on #affectedbeliefs! What are affected beliefs? Beliefs are never neutral – they always depend on the context, ...
Read More
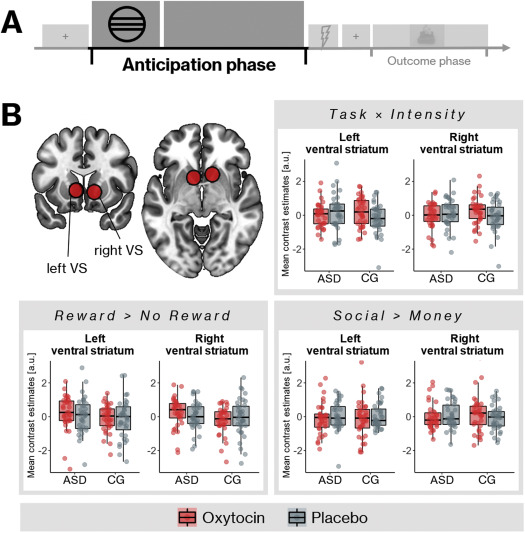
Assessment of reward-related brain function after a single-dose of oxytocin in autism: a randomized controlled trial
October 23, 2021
Biological Psychiatry: GOS
Background Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is characterized by difficulties in social communication and interaction, which have been related to atypical neural processing of rewards, especially ...
Read More
A psychological perspective on vicarious embarrassment and shame in the context of cringe humor
October 17, 2021
Humanities
Abstract Cringe humor combines the seemingly opposite emotional experiences of amusement and embarrassment due to others’ transgressions of norms. Psychological theories and empirical studies on ...
Read More
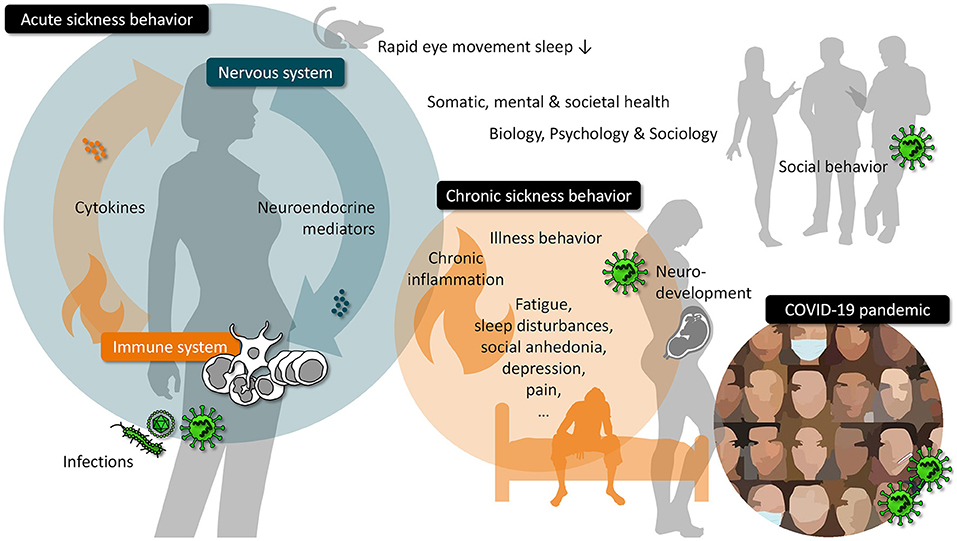
Editorial: The Different Faces of Sickness
September 1, 2021
Frontiers in Psychiatry
Editorial on the Research Topic: The Different Faces of Sickness Sickness not only includes symptoms that classically define an infection (e.g., fever, nausea, headache), ...
Read More
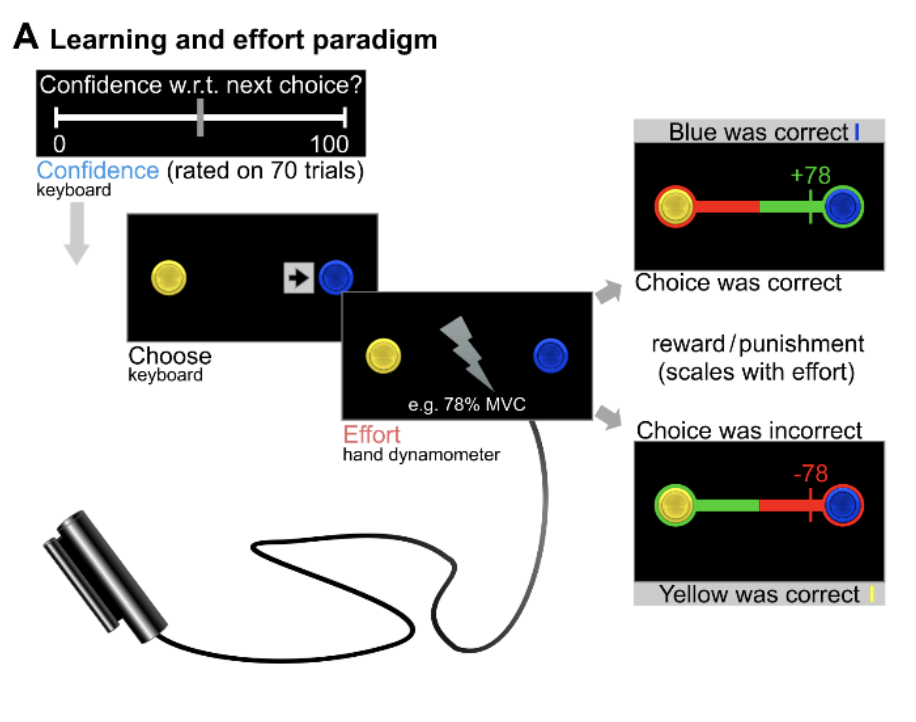
Reduced frontal cortical tracking of conflict between self-beneficial versus prosocial motives in Narcissistic Personality Disorder
August 28, 2021
NeuroImage: Clinical
Abstract Abstract Narcissistic Personality Disorder (NPD) entails severe impairments in interpersonal functioning that are likely driven by self-beneficial and exploitative behavior. Here, we investigate the ...
Read More